华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,光学与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
提出一种基于自外差探测技术的相干光载射频信号传输系统,可以借助自外差探测技术实现光学上变频。在该系统中,4个低频信号被上变频为高频毫米波信号,且在远端射频单元无需进行任何数字信号处理(DSP)。分析了对称边带串扰产生的原因并提出了在发射端消除边带串扰的方法。实验验证了通过在发射端使用4路独立、载频为10 GHz、带宽为1.6 GBaud的16-QAM射频信号和一个载频为20 GHz的单音信号,可以在接收端产生4路独立、载频为30 GHz、带宽为1.6 GBaud的16-QAM毫米波信号。在接收端不使用任何数字补偿算法的情况下,这4路毫米波信号经过50 km标准单模光纤传输后的误差矢量幅度(EVM)值均低于12.5%的阈值,复合速率达到25.6 Gbit/s。此外,发射端的数模转换采样率可以降至24 GSa/s,有效降低了系统的成本和复杂度。
光通信 模拟光载射频 毫米波通信 自外差相干探测 光学上变频 对称边带串扰 中国激光
2022, 49(12): 1206005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Engineering Laboratory for Next Generation Internet Access System (NGIA), School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), Wuhan 430074, China
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel physical layer encryption scheme for high-speed optical communication. A 10 Gb/s on-off keying signal is secretly transmitted over 100 km standard single-mode fiber. The intensity-modulated message is secured by the encryption mechanism, which is composed of an external noise source and an internal time-delayed feedback loop. The external noise serves as an entropy source with sufficient randomness. The feedback loop structure in the transmitter introduces a time-domain encryption key space, and a corresponding open-loop configuration at the receiver side is used for synchronization and decryption. Experiment results show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme. For a legitimate terminal, bit error rate below can be obtained. Decryption degradations with the mismatch of different hardware parameters are researched. The time delay in the feedback loop provides a sensitive encryption key. For other hardware parameters, the system is robust enough for synchronization. Meanwhile, the time-delay signature of the loop is able to be well concealed by the external noise. Moreover, the proposed scheme can support density wavelength division multiplexing transmission with a relatively simple structure. This work also provides a new concept to establish optical secure communication by combining a time-delayed feedback chaotic system and random noise.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(11): 11001306
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optical and Electrical Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
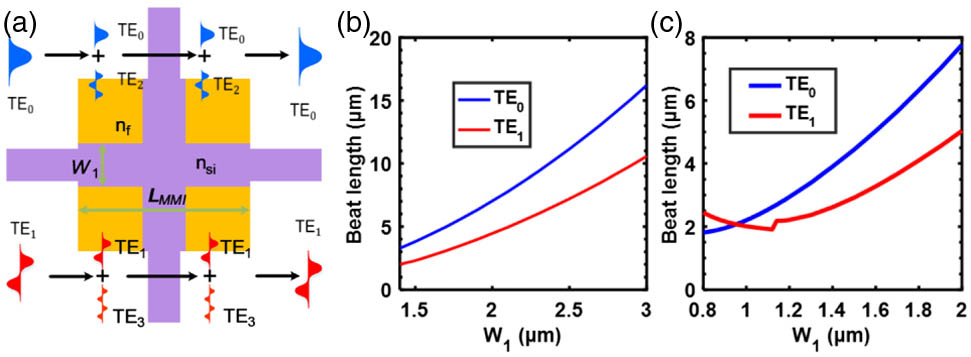
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel ultracompact dual-mode waveguide crossing based on subwavelength multimode-interference couplers for a densely integrated on-chip mode-division multiplexing system. By engineering the lateral-cladding material index and manipulating phase profiles of light at the nanoscale using an improved inverse design method, a subwavelength structure could theoretically realize the identical beat length for both TE0 and TE1, which can reduce the scale of the device greatly. The fabricated device occupied a footprint of only 4.8 μm×4.8 μm. The measured insertion losses and crosstalks were less than 0.6 dB and 24 dB from 1530 nm to 1590 nm for both TE0 and TE1 modes, respectively. Furthermore, our scheme could also be expanded to design waveguide crossings that support more modes.
Integrated optics devices Multiplexing Metamaterials Photonics Research
2018, 6(7): 07000660
Next Generation Internet Access National Engineering Laboratory (NGIA), School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2017, 10(4): 378
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The impulsive synchronization problem for semiconductor laser (SL) chaotic systems is studied. SL systems can be described by the rate equations governing photon density and carrier density. Because the carrier density is not easy to observe or measure, only photon density is used to design the impulsive controller. Several sufficient conditions for the synchronization of SL chaotic systems via impulsive control are derived. Numerical simulations are presented to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 140.1540 Chaos 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(10): 101901





